Your Guide to Prostate Health
Access evidence-based articles, expert insights, and comprehensive guides on prostate health for men at every stage of life. Stay informed with the latest research, prevention strategies, and wellness information.
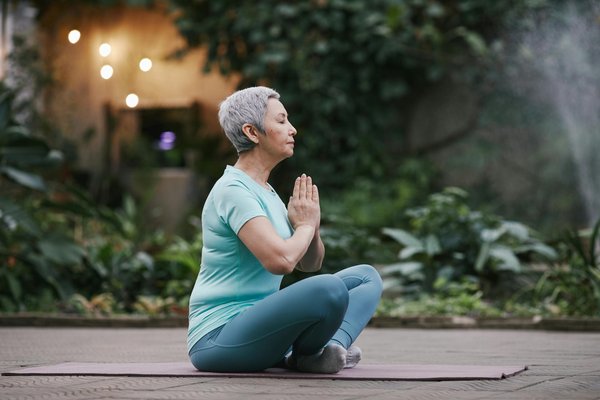

Explore Health Topics
Browse comprehensive guides and articles across all aspects of health and wellness
Latest articles
Our recent publications

Find your path to healing with professional mental health in dubai
Dubai's rapid growth has brought unique mental health challenges, with recent studies showing a 40% ...

Discover the best online pharmacy options in the uk
Finding a reliable online pharmacy in the UK can save time and ensure safe access to medications. Ch...

Enhancing productivity with hatchery automation technologies
Automation transforms hatcheries by streamlining egg handling, incubation, and chick processing. Int...

Unlock relaxation: the ultimate guide to back massage benefits
A back massage offers more than momentary relief—it promotes muscle relaxation, improves circulation...
Anti-aging aesthetic medicine in paris: personalized treatments for youthful skin
Experience tailored anti-aging treatments in Paris designed to rejuvenate your skin naturally. Combi...

Top orthopedic sandals for comfort and support in australia
Searching for the perfect blend of comfort and support in orthopedic sandals? You're in the right pl...
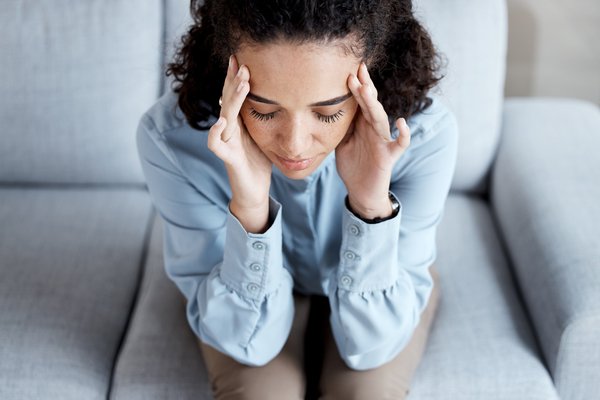

Practical strategies for effective anxiety management
Anxiety can be overwhelming, but it doesn't have to control your life. Understanding its origins and...

Discovering psychology: unlocking your mind's potential
Unlock the secrets of your mind and embrace the transformative power of psychology. This exploration...

How Does Precision Medicine Tailor Cancer Treatment to Individual Genetic Profiles?
...

What Is the Efficacy of Algae-Based Supplements in Reducing Inflammation?
As a savvy health-conscious reader, you may have come across a myriad of health-related articles or ...

What New Approaches Are Being Developed for Non-surgical Treatment of Glaucoma?
Glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness worldwide, significantly impacts the lives of millions of pat...

Can Enhancing Indoor Lighting Improve Mood and Productivity in Winter Months?
The winter months often bring shorter daylight hours, impacting mental health, mood, and productivit...

How Can Mindful Eating Practices Aid in the Treatment of Binge Eating Disorder?
Every day, you eat to sustain your body and mind, though often without awareness or intentionality. ...

What Are the Psychological Benefits of Regular Mountain Hiking?
...

How Can Text Message Reminders Improve Vaccination Rates in Rural Communities?
...

What Are the Latest Treatments for Hormone-Refractory Prostate Cancer?
...

What Are the Therapeutic Effects of Deep Tissue Massage on Chronic Lower Back Pain?
Massage therapy has emerged as an effective method for alleviating various types of pain, particular...
How Can UK Pregnant Women Evaluate and Choose the Right Maternity Services?
...

What Are the Protocols in the UK for Treating Pregnancy-Related Pelvic Girdle Pain?
...

What Are the Safe and Recommended Types of Fish for UK Pregnant Women to Consume?
...

Can UK optometrists utilize advanced corneal mapping to improve outcomes in corneal transplant surgeries?
Corneal transplant surgeries, also known as corneal grafting, is a surgical procedure that replaces ...

How can UK clinical pharmacists help manage complex medication regimens in elderly patients with chronic illnesses?
...
What are the innovative non-drug approaches UK rheumatologists are using for managing systemic lupus erythematosus?
...

How Can Seniors Over 85 Safely Increase Social Interaction Without Leaving Their Home?
...

How Can Seniors Utilize Podcasts for Entertainment and Education?
Podcasts have exploded in popularity over the past few years. They've become a new form of radio, of...

What Are Essential Safety Tips for Seniors Who Live Alone and Rely on Home Care Services?
...

Can Participating in Community Theatre Productions Improve Social Skills in UK Adolescents?
...

How Does the Nutrient Profile of UK-Grown Quinoa Compare with Imported Varieties?
...

What Is the Best Approach to Learning and Practicing Mindfulness Meditation for UK Beginners?
Learning and practicing mindfulness meditation is an enlightening journey and a powerful tool for pe...
How to Choose the Correct HEPA Air Purifier for Allergy Sufferers?
As allergy sufferers, you understand that keeping your indoor environment clean is critical for your...
Stay Informed About Your Health
Explore our extensive library of articles, research summaries, and wellness guides to make informed decisions about prostate health and overall wellbeing. Learn more at https://philippejacquet.co.uk.
Rejoindre →